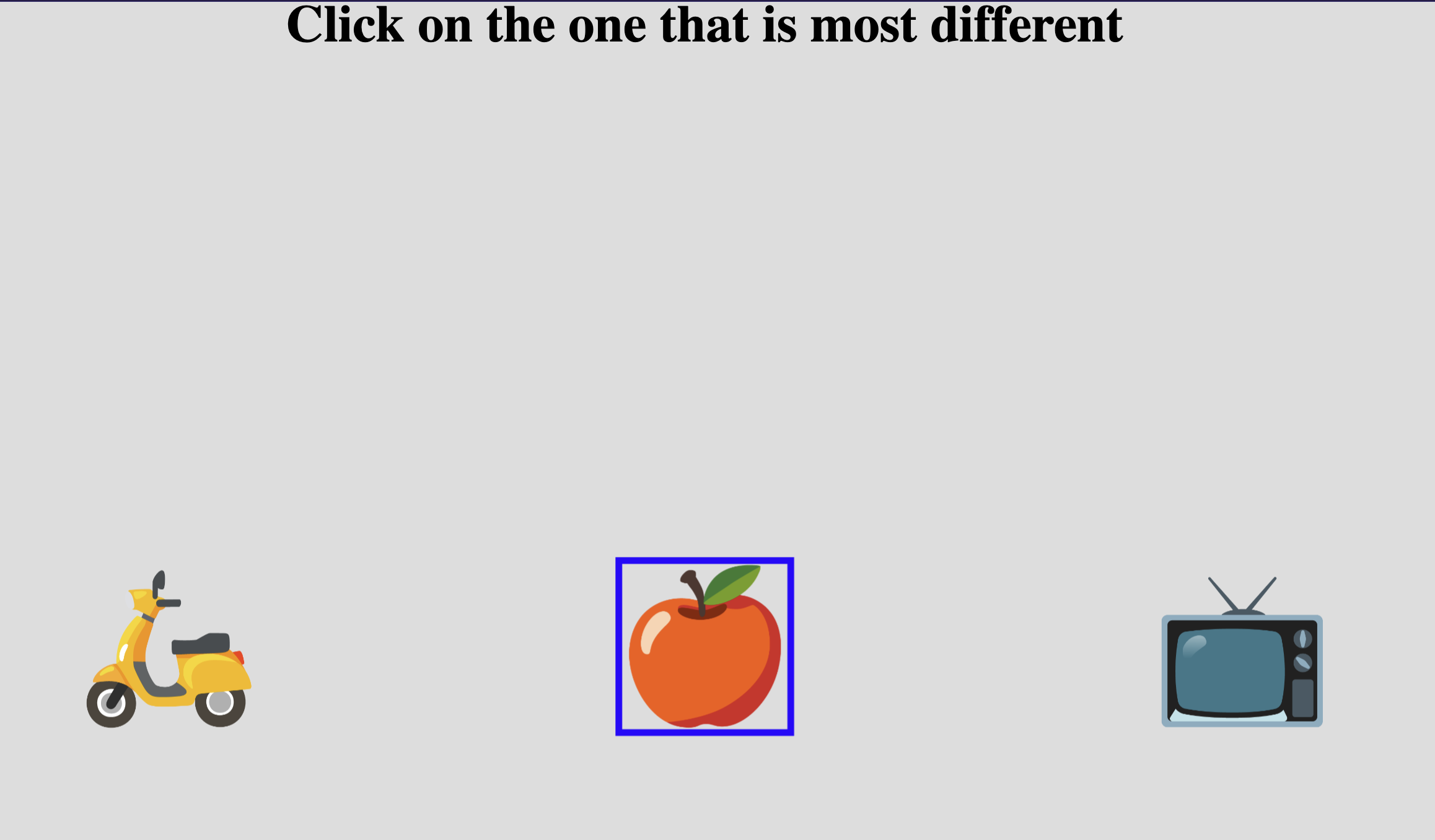
Triplet Choice Task¶
The Triplet Choice task presents three stimuli simultaneously, from which the participant selects one by clicking it. This paradigm is commonly used to obtain similarity judgments by asking participants to select the "odd one out" - the stimulus that is most different from the other two.
The triplet task (also known as the odd-one-out task, or three-alternative forced choice, 3AFC) is an popular method for collecting similarity data, as each trial provides information about the relative similarity among three items. This approach has been widely used in perceptual and cognitive research to study how people judge similarity across various stimulus domains including images, sounds, and text12.
Example Triplet Choice task with three stimuli presented. The apple is selected as the "odd-one-out".
Below you'll find information specific to the Triplet Choice task. This assumes you're familiar with how to setup an experiment and how to select stimuli for a given task.
Parameters¶
Customize the task by changing these on the Parameters tab of the task.
General Interface settings¶
Customize the instruction at the top of the page, as well as toolbar buttons. These apply to most task types on Meadows.
Instruction hint-
Text that you can display during the task at the top of the page.
Extended instruction-
A longer instruction that only appears if the participant hovers their mouse cursor over the hint.
Tip
Make clear to participants what criterion they should use for selecting the odd one out. For example: "Click on the image that looks most different from the other two" or "Select the sound that doesn't belong with the other two."
Hint size-
Whether to display the instruction, or hide it, and what font size to use.
Fullscreen button-
Whether to display a button in the bottom toolbar that participants can use to switch fullscreen mode on and off.
Trials and stimuli¶
Control the number of trials and how stimuli are combined into triplets.
Tip
If you don't want the task to automatically generate trials, but instead prefer to sample them yourself, you can use a Trial File.
Maximum Number Of Trials-
The number of trials will equal the total number of unique combinations of stimuli (choosing 3 at a time), or this parameter, whichever is smaller. Default: 50. Must be between 1 and 1000.
Trial generation
For n stimuli, there are n×(n-1)×(n-2)/6 unique unordered triplets. For example, 10 stimuli yield 120 possible triplets, while 20 stimuli yield 1140 triplets. The task will sample from these combinations up to the maximum specified.
Proportion Of Trials With Double-
How many of the total number of trials should be "catch trials" with the same stimulus shown twice (making the odd-one-out task trivial). This can be used to check participant attention. Default: 0.3 (30%). Must be between 0.0 and 0.9.
Example
With this set to 0.3 and 50 trials total, approximately 15 trials will show the same stimulus twice, making one clearly different and easy to identify.
Shuffle Trial-
Randomize the left-to-right order of the three stimuli in each trial. Default: False. This is relevant only for trial-file or balanced-sampling based setups where you want to control which stimuli appear together but randomize their positions.
Blank Duration-
Duration in milliseconds to show a blank screen between trials. Set to 0 to turn this off. Default: 500 ms. Must be between 0 and 5000 ms.
Minimum Trial Duration-
The stimuli will be displayed for at least this duration (in milliseconds), even if a response was given earlier. This ensures participants view the stimuli for a minimum amount of time. Default: 0 ms. Must be between 0 and 10,000 ms.
Cannot Confirm Trial Until All Audio/Video Stimuli Have Finished-
If enabled, participants must wait for all audio or video stimuli to finish playing before they can confirm their selection. Default: False.
Wait Button Text-
Caption of the submit button when the trial is not ready yet (e.g., minimum duration not reached, or media still playing). Default: "wait..". Max 20 characters.
Spatial configuration¶
Options for customizing the layout of stimuli on the screen.
Item Size-
Height of the stimuli. Default: 8.0. Must be between 0.2 and 40.0. The width is adapted according to the original aspect ratio of the stimulus.
Item Unit-
The unit to use for the size of the stimuli. Options:
- Percentage of the available width (default)
- Centimeters - requires participant calibration
- Visual angle in Degrees - requires participant calibration and distance measurement
See the documentation page "Dimensions, Units & Calibration" for more details.
Visual feedback¶
Target Outline Thickness-
Width (in pixels) of the border displayed around the selected stimulus. Set to 0 for no outline. Default: 0. Must be between 0 and 50.
Target Outline Color-
Color of the border around the selected stimulus. Options: Red, Green, Blue, Black, White. Default: Red.
Data¶
For general information about the various structures and file formats that you can download for your data see Downloads.
Triplet-wise "annotations" (table rows). Each row represents one trial. Columns:
taskName of the taskparticipationName of the experiment/participationtrialNumerical index of the trial (starting from 0)time_trial_startTimestamp when the trial was displayed (seconds since 1/1/1970)time_trial_responseTimestamp when the participant confirmed their selectionstim1_idMeadows internal ID of the first stimulusstim1_nameFilename of the first stimulus as uploadedstim2_idMeadows internal ID of the second stimulusstim2_nameFilename of the second stimulus as uploadedstim3_idMeadows internal ID of the third stimulusstim3_nameFilename of the third stimulus as uploadedlabelID of the stimulus that was selected as the odd one out
In the Tree structure, under the task object:
annotationsAn array with a key/value map for each trial:trialNumerical index of the trialstartTimestamp (epoch time) of the start of the trial, in seconds since 1/1/1970respTimestamp (epoch time) of the response, in seconds since 1/1/1970idsArray of three stimulus IDs presented in this triallabelThe ID of the stimulus selected as odd one out
stimuliArray of stimulus objects withidandnamefields
Analysis and Visualization¶
The triplet task data can be analyzed to construct similarity matrices or train computational models of similarity.
Computing similarity from odd-one-out judgments¶
When a participant selects stimulus C as the odd one out from triplet (A, B, C), this implies that A and B are more similar to each other than either is to C. This information can be aggregated across trials to estimate pairwise similarities2.
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
# Load annotations data
df = pd.read_csv('Meadows_myExperiment_v1_annotations.csv')
# Get unique stimuli
stimuli = pd.unique(df[['stim1_name', 'stim2_name', 'stim3_name']].values.ravel())
n_stim = len(stimuli)
stim_to_idx = {s: i for i, s in enumerate(stimuli)}
# Initialize similarity matrix (higher = more similar)
similarity = np.zeros((n_stim, n_stim))
# For each trial, the two non-selected stimuli are more similar
for _, row in df.iterrows():
triplet = [row['stim1_name'], row['stim2_name'], row['stim3_name']]
odd_one = next(s for s in [row['stim1_name'], row['stim2_name'],
row['stim3_name']] if row['label'] in str(s))
# The pair that wasn't selected as odd are more similar
similar_pair = [s for s in triplet if s != odd_one]
if len(similar_pair) == 2:
i, j = stim_to_idx[similar_pair[0]], stim_to_idx[similar_pair[1]]
similarity[i, j] += 1
similarity[j, i] += 1
# Visualize
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 8))
plt.imshow(similarity, cmap='viridis')
plt.colorbar(label='Similarity score')
plt.xticks(range(n_stim), stimuli, rotation=90)
plt.yticks(range(n_stim), stimuli)
plt.title('Pairwise Similarity from Triplet Judgments')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
library(ggplot2)
# Load data
df <- read.csv('Meadows_myExperiment_v1_annotations.csv')
# Calculate reaction time in seconds
df$rt_seconds <- df$time_trial_response - df$time_trial_start
# Plot distribution
ggplot(df, aes(x = rt_seconds)) +
geom_histogram(bins = 30, fill = "steelblue", color = "black") +
labs(x = "Reaction Time (seconds)",
y = "Frequency",
title = "Distribution of Reaction Times in Triplet Task") +
theme_minimal()
# Summary statistics
cat(sprintf("Mean RT: %.2f seconds\n", mean(df$rt_seconds)))
cat(sprintf("Median RT: %.2f seconds\n", median(df$rt_seconds)))
References¶
-
Zheng, C. Y., Pereira, F., Baker, C. I., & Hebart, M. N. (2019). Revealing interpretable object representations from human behavior. International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR). arXiv:1901.02915 ↩
-
Roads, B. D., & Love, B. C. (2021). Enriching ImageNet with Human Similarity Judgments and Psychological Embeddings. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 3547-3557. doi:10.1109/CVPR46437.2021.00355 ↩↩